Gusdorff, Jordan A.; Bhatia, Pia; Shin, Trey T.; Uy-Tioco, Alexandra Sofia; Sailors, Benjamin N.; Keneipp, Rachael N.; Drndić, Marija; Bassett, Lee C.
Correlated Structural and Optical Characterization of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, vol. 9, iss. 11, pp. 11100-11110, 2025.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 2-dimensional systems, Materials Physics, photoluminescence
@article{Gusdorff2025,
title = {Correlated Structural and Optical Characterization of Hexagonal Boron Nitride},
author = {Jordan A. Gusdorff and Pia Bhatia and Trey T. Shin and Alexandra Sofia Uy-Tioco and Benjamin N. Sailors and Rachael N. Keneipp and Marija Drndić and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.4c17676
https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.14408},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.4c17676},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-02-21},
urldate = {2025-02-21},
journal = {ACS Nano},
volume = {9},
issue = {11},
pages = {11100-11110},
abstract = {Hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) hosts quantum emitters that exhibit single-photon emission and spin-dependent fluorescence at room temperature. These features make hBN a promising platform for quantum sensing and photonics. Despite many investigations of their optical properties, the emitters' chemical structure remains unclear, as does the role of contamination at surfaces and interfaces in forming the emitters or modifying their properties. We prepare hBN samples that are compatible with both confocal photoluminescence microscopy (PL) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and we use those techniques to investigate correlations between fluorescent emission, flake morphology, and surface residue. We find that the microscopy techniques themselves induce changes in hBN's optical activity and residue morphology: PL measurements induce photobleaching, whereas TEM measurements alter surface residue and emission characteristics. We also study the effects of common treatments — annealing and oxygen plasma cleaning — on the structure and optical activity of hBN. The results illustrate the power and importance of correlative studies to elucidate aspects of microscopic mechanisms that influence hBN's functionality as a host for quantum emitters and spin defects.},
keywords = {2-dimensional systems, Materials Physics, photoluminescence},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
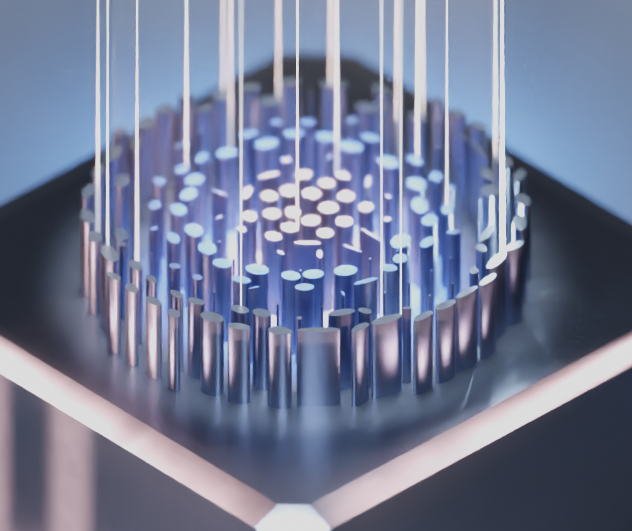
Klein, Amelia R.; Engheta, Nader; Bassett, Lee C.
Designing metasurface optical interfaces for solid-state qubits using many-body adjoint shape optimization Journal Article
In: Optics Express, vol. 32, iss. 22, pp. 38504-38515, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: diamond fabrication, diamond NV center, Nanophotonics, photoluminescence
@article{Klein2024,
title = {Designing metasurface optical interfaces for solid-state qubits using many-body adjoint shape optimization},
author = {Amelia R. Klein and Nader Engheta and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://opg.optica.org/oe/fulltext.cfm?uri=oe-32-22-38504&id=561330
https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.08212},
doi = {10.1364/OE.522501},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-09},
urldate = {2024-10-09},
journal = {Optics Express},
volume = {32},
issue = {22},
pages = {38504-38515},
abstract = {We present a general strategy for the inverse design of metasurfaces composed of elementary shapes. We use it to design a structure that collects and collimates light from nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond. Such metasurfaces constitute scalable optical interfaces for solid-state qubits, enabling efficient photon coupling into optical fibers and eliminating free-space collection optics. The many-body shape optimization strategy is a practical alternative to topology optimization that explicitly enforces material and fabrication constraints throughout the optimization, while still achieving high performance. The metasurface is easily adaptable to other solid-state qubits, and the optimization method is broadly applicable to fabrication-constrained photonic design problems.},
keywords = {diamond fabrication, diamond NV center, Nanophotonics, photoluminescence},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
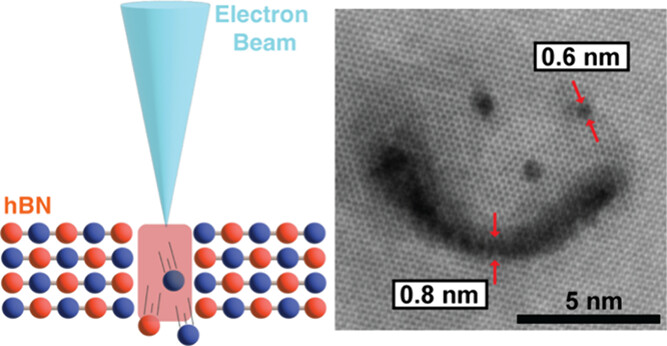
Keneipp, Rachael N.; Gusdorff, Jordan A.; Bhatia, Pia; Shin, Trey T.; Bassett, Lee C.; Drndić, Marija
Nanoscale Sculpting of Hexagonal Boron Nitride with an Electron Beam Journal Article
In: Journal of Physical Chemistry C, vol. 128, no. 21, pp. 8741–8749, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 2-dimensional systems, color centers, photoluminescence, point defects
@article{Keneipp2024,
title = {Nanoscale Sculpting of Hexagonal Boron Nitride with an Electron Beam},
author = {Rachael N. Keneipp and Jordan A. Gusdorff and Pia Bhatia and Trey T. Shin and Lee C. Bassett and Marija Drndić},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c02038},
doi = {10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c02038},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-05-17},
journal = {Journal of Physical Chemistry C},
volume = {128},
number = {21},
pages = {8741–8749},
abstract = {Creating sub- to few-nanometer defects and nanopores in hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) opens opportunities for engineering quantum emitters and for nanofluidic and sensing applications. Using the electron beam in the aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscope, we demonstrate modification, thinning, and drilling of features in few-layer hBN membranes (∼5 to 20 nm-thick). The atomic composition is monitored with electron energy loss spectroscopy, which also facilitates drift correction. We report effects of electron beam energy and exposure times on defect size and structure. While previous studies focused on beam energies of ≤80 keV to avoid material damage, we show that drilling is favorable at a higher beam energy of 200 keV. The drilling rate at 200 keV is about 10 times larger than at 80 keV (∼1.2 vs 0.1 nm/min), and smaller pores are achievable with minimized damage to the surrounding material. Thinned hBN nanoscale features demonstrate enhanced emission via photoluminescence spectroscopy.},
keywords = {2-dimensional systems, color centers, photoluminescence, point defects},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
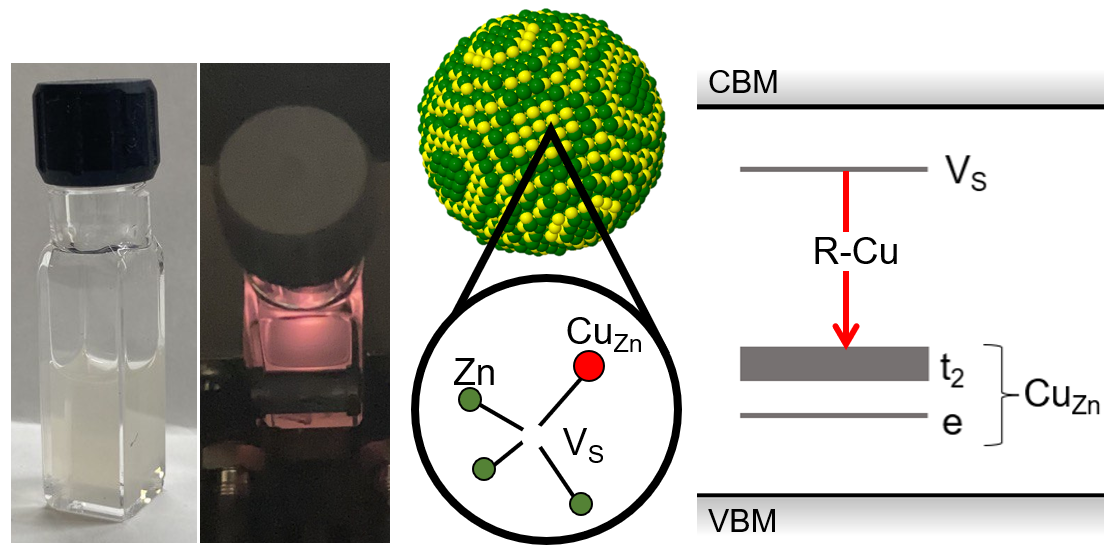
Thompson, Sarah M.; Şahin, Cüneyt; Yang, Shengsong; Flatté, Michael E.; Murray, Christopher B.; Bassett, Lee C.; Kagan, Cherie R.
Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, 2023.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: colloidal nanocrystals, color centers, First-principles calculations, impurity doping, Materials Physics, nanocrystals, photoluminescence, quantum dots, transition metals, ZnS
@article{Thompson2023,
title = {Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals},
author = {Sarah M. Thompson and Cüneyt Şahin and Shengsong Yang and Michael E. Flatté and Christopher B. Murray and Lee C. Bassett and Cherie R. Kagan},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.3c00191
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.04223},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.3c00191},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-03-09},
journal = {ACS Nano},
abstract = {Copper-doped zinc sulfide (ZnS:Cu) exhibits down-conversion luminescence in the UV, visible, and IR regions of the electromagnetic spectrum; the visible red, green, and blue emission is referred to as R-Cu, G-Cu, and B-Cu, respectively. The sub-bandgap emission arises from optical transitions between localized electronic states created by point defects, making ZnS:Cu a prolific phosphor material and an intriguing candidate material for quantum information science, where point defects excel as single-photon sources and spin qubits. Colloidal nanocrystals (NCs) of ZnS:Cu are particularly interesting as hosts for the creation, isolation, and measurement of quantum defects, since their size, composition, and surface chemistry can be precisely tailored for bio-sensing and opto-electronic applications. Here, we present a method for synthesizing colloidal ZnS:Cu NCs that emit primarily R-Cu, which has been proposed to arise from the CuZn-VS complex, an impurity-vacancy point defect structure analogous to well-known quantum defects in other materials that produce favorable optical and spin dynamics. First principles calculations confirm the thermodynamic stability and electronic structure of CuZn-VS. Temperature- and time-dependent optical properties of ZnS:Cu NCs show blueshifting luminescence and an anomalous plateau in the intensity dependence as temperature is increased from 19 K to 290 K, for which we propose an empirical dynamical model based on thermally-activated coupling between two manifolds of states inside the ZnS bandgap. Understanding of R-Cu emission dynamics, combined with a controlled synthesis method for obtaining R-Cu centers in colloidal NC hosts, will greatly facilitate the development of CuZn-VS and related complexes as quantum point defects in ZnS.},
keywords = {colloidal nanocrystals, color centers, First-principles calculations, impurity doping, Materials Physics, nanocrystals, photoluminescence, quantum dots, transition metals, ZnS},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2025

Gusdorff, Jordan A.; Bhatia, Pia; Shin, Trey T.; Uy-Tioco, Alexandra Sofia; Sailors, Benjamin N.; Keneipp, Rachael N.; Drndić, Marija; Bassett, Lee C.
Correlated Structural and Optical Characterization of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, vol. 9, iss. 11, pp. 11100-11110, 2025.
@article{Gusdorff2025,
title = {Correlated Structural and Optical Characterization of Hexagonal Boron Nitride},
author = {Jordan A. Gusdorff and Pia Bhatia and Trey T. Shin and Alexandra Sofia Uy-Tioco and Benjamin N. Sailors and Rachael N. Keneipp and Marija Drndić and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.4c17676
https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.14408},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.4c17676},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-02-21},
urldate = {2025-02-21},
journal = {ACS Nano},
volume = {9},
issue = {11},
pages = {11100-11110},
abstract = {Hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) hosts quantum emitters that exhibit single-photon emission and spin-dependent fluorescence at room temperature. These features make hBN a promising platform for quantum sensing and photonics. Despite many investigations of their optical properties, the emitters' chemical structure remains unclear, as does the role of contamination at surfaces and interfaces in forming the emitters or modifying their properties. We prepare hBN samples that are compatible with both confocal photoluminescence microscopy (PL) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and we use those techniques to investigate correlations between fluorescent emission, flake morphology, and surface residue. We find that the microscopy techniques themselves induce changes in hBN's optical activity and residue morphology: PL measurements induce photobleaching, whereas TEM measurements alter surface residue and emission characteristics. We also study the effects of common treatments — annealing and oxygen plasma cleaning — on the structure and optical activity of hBN. The results illustrate the power and importance of correlative studies to elucidate aspects of microscopic mechanisms that influence hBN's functionality as a host for quantum emitters and spin defects.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2024

Klein, Amelia R.; Engheta, Nader; Bassett, Lee C.
Designing metasurface optical interfaces for solid-state qubits using many-body adjoint shape optimization Journal Article
In: Optics Express, vol. 32, iss. 22, pp. 38504-38515, 2024.
@article{Klein2024,
title = {Designing metasurface optical interfaces for solid-state qubits using many-body adjoint shape optimization},
author = {Amelia R. Klein and Nader Engheta and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://opg.optica.org/oe/fulltext.cfm?uri=oe-32-22-38504&id=561330
https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.08212},
doi = {10.1364/OE.522501},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-09},
urldate = {2024-10-09},
journal = {Optics Express},
volume = {32},
issue = {22},
pages = {38504-38515},
abstract = {We present a general strategy for the inverse design of metasurfaces composed of elementary shapes. We use it to design a structure that collects and collimates light from nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond. Such metasurfaces constitute scalable optical interfaces for solid-state qubits, enabling efficient photon coupling into optical fibers and eliminating free-space collection optics. The many-body shape optimization strategy is a practical alternative to topology optimization that explicitly enforces material and fabrication constraints throughout the optimization, while still achieving high performance. The metasurface is easily adaptable to other solid-state qubits, and the optimization method is broadly applicable to fabrication-constrained photonic design problems.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Keneipp, Rachael N.; Gusdorff, Jordan A.; Bhatia, Pia; Shin, Trey T.; Bassett, Lee C.; Drndić, Marija
Nanoscale Sculpting of Hexagonal Boron Nitride with an Electron Beam Journal Article
In: Journal of Physical Chemistry C, vol. 128, no. 21, pp. 8741–8749, 2024.
@article{Keneipp2024,
title = {Nanoscale Sculpting of Hexagonal Boron Nitride with an Electron Beam},
author = {Rachael N. Keneipp and Jordan A. Gusdorff and Pia Bhatia and Trey T. Shin and Lee C. Bassett and Marija Drndić},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c02038},
doi = {10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c02038},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-05-17},
journal = {Journal of Physical Chemistry C},
volume = {128},
number = {21},
pages = {8741–8749},
abstract = {Creating sub- to few-nanometer defects and nanopores in hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) opens opportunities for engineering quantum emitters and for nanofluidic and sensing applications. Using the electron beam in the aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscope, we demonstrate modification, thinning, and drilling of features in few-layer hBN membranes (∼5 to 20 nm-thick). The atomic composition is monitored with electron energy loss spectroscopy, which also facilitates drift correction. We report effects of electron beam energy and exposure times on defect size and structure. While previous studies focused on beam energies of ≤80 keV to avoid material damage, we show that drilling is favorable at a higher beam energy of 200 keV. The drilling rate at 200 keV is about 10 times larger than at 80 keV (∼1.2 vs 0.1 nm/min), and smaller pores are achievable with minimized damage to the surrounding material. Thinned hBN nanoscale features demonstrate enhanced emission via photoluminescence spectroscopy.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2023

Thompson, Sarah M.; Şahin, Cüneyt; Yang, Shengsong; Flatté, Michael E.; Murray, Christopher B.; Bassett, Lee C.; Kagan, Cherie R.
Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, 2023.
@article{Thompson2023,
title = {Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals},
author = {Sarah M. Thompson and Cüneyt Şahin and Shengsong Yang and Michael E. Flatté and Christopher B. Murray and Lee C. Bassett and Cherie R. Kagan},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.3c00191
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.04223},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.3c00191},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-03-09},
journal = {ACS Nano},
abstract = {Copper-doped zinc sulfide (ZnS:Cu) exhibits down-conversion luminescence in the UV, visible, and IR regions of the electromagnetic spectrum; the visible red, green, and blue emission is referred to as R-Cu, G-Cu, and B-Cu, respectively. The sub-bandgap emission arises from optical transitions between localized electronic states created by point defects, making ZnS:Cu a prolific phosphor material and an intriguing candidate material for quantum information science, where point defects excel as single-photon sources and spin qubits. Colloidal nanocrystals (NCs) of ZnS:Cu are particularly interesting as hosts for the creation, isolation, and measurement of quantum defects, since their size, composition, and surface chemistry can be precisely tailored for bio-sensing and opto-electronic applications. Here, we present a method for synthesizing colloidal ZnS:Cu NCs that emit primarily R-Cu, which has been proposed to arise from the CuZn-VS complex, an impurity-vacancy point defect structure analogous to well-known quantum defects in other materials that produce favorable optical and spin dynamics. First principles calculations confirm the thermodynamic stability and electronic structure of CuZn-VS. Temperature- and time-dependent optical properties of ZnS:Cu NCs show blueshifting luminescence and an anomalous plateau in the intensity dependence as temperature is increased from 19 K to 290 K, for which we propose an empirical dynamical model based on thermally-activated coupling between two manifolds of states inside the ZnS bandgap. Understanding of R-Cu emission dynamics, combined with a controlled synthesis method for obtaining R-Cu centers in colloidal NC hosts, will greatly facilitate the development of CuZn-VS and related complexes as quantum point defects in ZnS.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Select publications before 2014
- “All-optical control of a solid-state spin using coherent dark states”, C. G. Yale, B. B. Buckley, D. J. Christle, G. Burkard, F. J. Heremans, L. C. Bassett, and D. D. Awschalom, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 7595 (2013).
- “Quantum spintronics: Engineering and manipulating atom-like spins in semiconductors”, D.D. Awschalom, L.C. Bassett, A.S. Dzurak, E.L. Hu and J.R. Petta, Science 339, 1174 (2013).
Related article: “The Future of Quantum Information Processing”, J. Stajic, Science 339, 1163 (2013).
- “Engineering and quantum control of single spins in semiconductors”, D.M. Toyli, L.C. Bassett, B.B. Buckley, G. Calusine and D.D. Awschalom, MRS Bulletin 38, 139 (2013).
- “Engineering shallow spins in diamond with nitrogen delta-doping”, K. Ohno, F. J. Heremans, L. C. Bassett, B. A. Myers, D. M. Toyli, A. C. Bleszynski-Jayich, C. J. Palmstrøm, and D. D. Awschalom, Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 082413 (2012).
- “Electrical tuning of single nitrogen-vacancy center optical transitions enhanced by photoinduced fields”, L. C. Bassett, F. J. Heremans, C. G. Yale, B. B. Buckley, and D. D. Awschalom, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 266403 (2011).
- “Spin-light coherence for single-spin measurement and control in diamond”, B. B. Buckley, G. D. Fuchs, L. C. Bassett, and D. D. Awschalom, Science 330, 1212 (2010).
Related article: “Quantum measurement and control of single spins in diamond”, Science 330, 1188 (2010).