Panfil, Yossef E.; Thompson, Sarah M.; Chen, Gary; Ng, Jonah; Kagan, Cherie R.; Bassett, Lee C.
Room-temperature quantum emission from CuZn-VS defects in ZnS:Cu colloidal nanocrystals Journal Article Forthcoming
In: ACS Nano, Forthcoming.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: colloidal nanocrystals, forthcoming, quantum defects, ZnS
@article{Panfil2025,
title = {Room-temperature quantum emission from CuZn-VS defects in ZnS:Cu colloidal nanocrystals},
author = {Yossef E. Panfil and Sarah M. Thompson and Gary Chen and Jonah Ng and Cherie R. Kagan and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsnano.5c01265
https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.11812},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-06-05},
urldate = {2025-01-21},
journal = {ACS Nano},
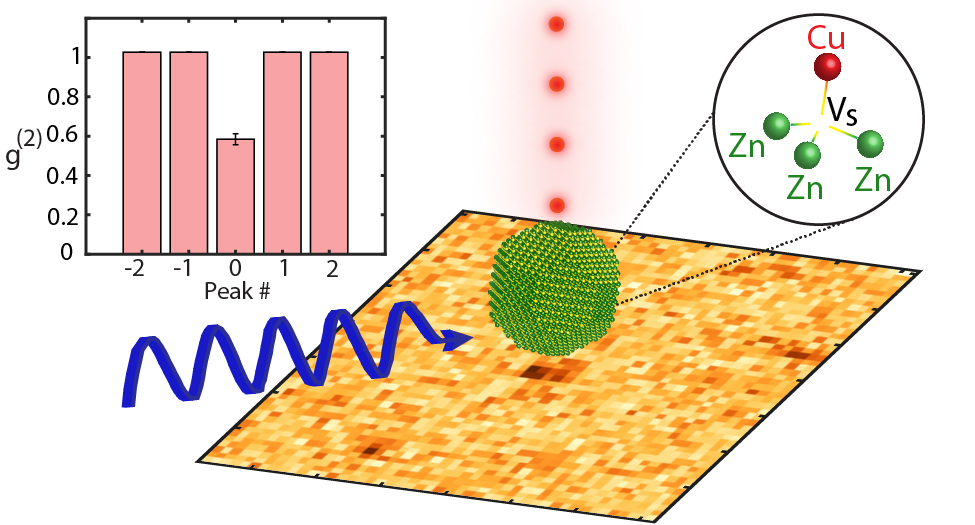
abstract = {We report room-temperature observations of CuZn-VS quantum emitters in individual ZnS:Cu nanocrystals (NCs). Using time-gated imaging, we isolate the distinct, ∼3-μs-long, red photoluminescence (PL) emission of CuZn-VS defects, enabling their precise identification and statistical characterization. The emitters exhibit distinct blinking and photon antibunching, consistent with individual NCs containing two to four CuZn-VS defects. The quantum emitters' PL spectra show a pronounced blue shift compared to NC dispersions, likely due to photochemical and charging effects. Emission polarization measurements of quantum emitters are consistent with a σ-character optical dipole transition and the symmetry of the CuZn-VS defect. These observations motivate further investigation of CuZn-VS defects in ZnS NCs for use in quantum technologies.},
keywords = {colloidal nanocrystals, forthcoming, quantum defects, ZnS},
pubstate = {forthcoming},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Shulevitz, Henry J.; Amirshaghaghi, Ahmad; Ouellet, Mathieu; Brustoloni, Caroline; Yang, Shengsong; Ng, Jonah J.; Huang, Tzu-Yung; Jishkariani, Davit; Murray, Christopher B.; Tsourkas, Andrew; Kagan, Cherie R.; Bassett, Lee C.
Nanodiamond emulsions for enhanced quantum sensing and click-chemistry conjugation Journal Article
In: ACS Applied Nano Materials, vol. 7, iss. 13, pp. 15334-15343, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: colloidal nanocrystals, diamond NV center, nanodiamonds, spin relaxometry
@article{Shulevitz2024,
title = {Nanodiamond emulsions for enhanced quantum sensing and click-chemistry conjugation},
author = {Henry J. Shulevitz and Ahmad Amirshaghaghi and Mathieu Ouellet and Caroline Brustoloni and Shengsong Yang and Jonah J. Ng and Tzu-Yung Huang and Davit Jishkariani and Christopher B. Murray and Andrew Tsourkas and Cherie R. Kagan and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsanm.4c01699
https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.16530},
doi = {10.1021/acsanm.4c01699},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-06-29},
urldate = {2024-06-29},
journal = {ACS Applied Nano Materials},
volume = {7},
issue = {13},
pages = {15334-15343},
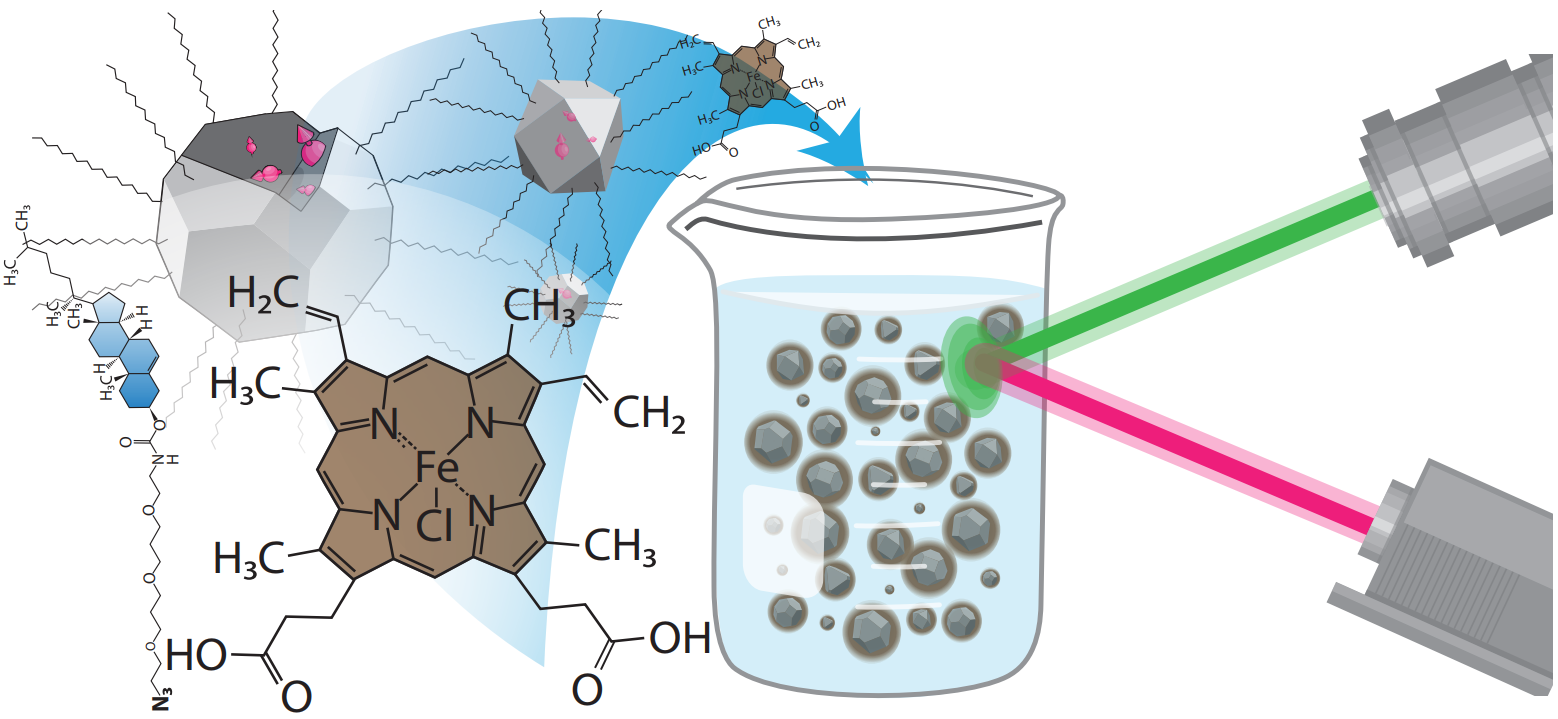
abstract = {Nanodiamonds containing nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers can serve as colloidal quantum sensors of local fields in biological and chemical environments. However, nanodiamond surfaces are challenging to modify without degrading their colloidal stability or the NV center’s optical and spin properties. We present a simple and general method to coat nanodiamonds with a thin emulsion layer that preserves their quantum features, maintains their colloidal stability, and provides functional groups for subsequent cross-linking and click-chemistry conjugation reactions. To demonstrate this technique, we decorated nanodiamonds with combinations of carboxyl- and azide-terminated amphiphiles that enable conjugation using two different strategies. A theoretical model is developed to understand the effect of the emulsion layer on the NV center’s spin lifetime, and T1 relaxometry is employed to quantify the nanodiamonds’ chemical sensitivity to paramagnetic ions. This general approach to nanodiamond surface functionalization will enable advances in quantum nanomedicine and biological sensing.},
keywords = {colloidal nanocrystals, diamond NV center, nanodiamonds, spin relaxometry},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Thompson, Sarah M.; Şahin, Cüneyt; Yang, Shengsong; Flatté, Michael E.; Murray, Christopher B.; Bassett, Lee C.; Kagan, Cherie R.
Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, 2023.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: colloidal nanocrystals, color centers, First-principles calculations, impurity doping, Materials Physics, nanocrystals, photoluminescence, quantum dots, transition metals, ZnS
@article{Thompson2023,
title = {Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals},
author = {Sarah M. Thompson and Cüneyt Şahin and Shengsong Yang and Michael E. Flatté and Christopher B. Murray and Lee C. Bassett and Cherie R. Kagan},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.3c00191
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.04223},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.3c00191},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-03-09},
journal = {ACS Nano},
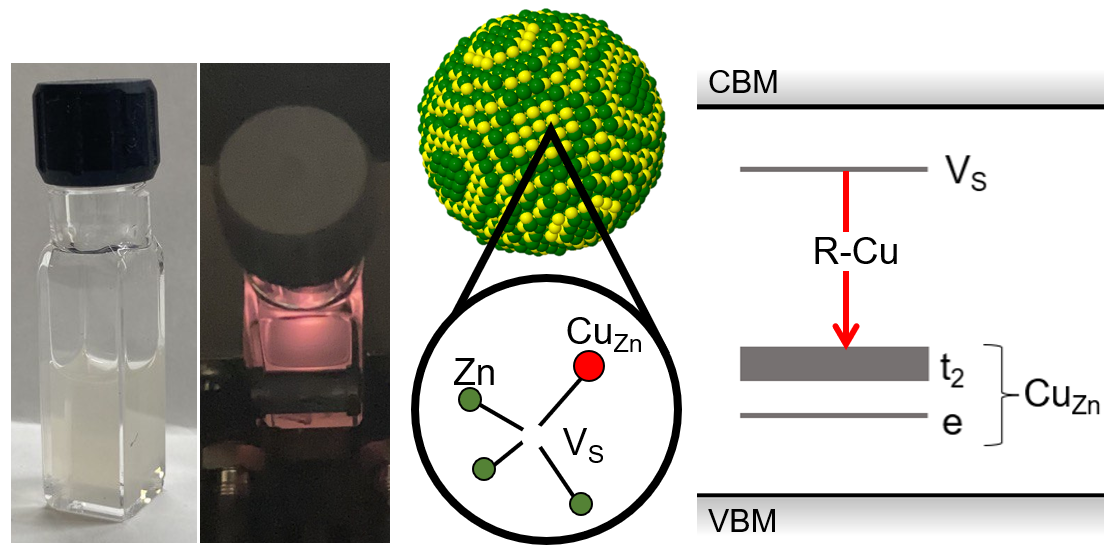
abstract = {Copper-doped zinc sulfide (ZnS:Cu) exhibits down-conversion luminescence in the UV, visible, and IR regions of the electromagnetic spectrum; the visible red, green, and blue emission is referred to as R-Cu, G-Cu, and B-Cu, respectively. The sub-bandgap emission arises from optical transitions between localized electronic states created by point defects, making ZnS:Cu a prolific phosphor material and an intriguing candidate material for quantum information science, where point defects excel as single-photon sources and spin qubits. Colloidal nanocrystals (NCs) of ZnS:Cu are particularly interesting as hosts for the creation, isolation, and measurement of quantum defects, since their size, composition, and surface chemistry can be precisely tailored for bio-sensing and opto-electronic applications. Here, we present a method for synthesizing colloidal ZnS:Cu NCs that emit primarily R-Cu, which has been proposed to arise from the CuZn-VS complex, an impurity-vacancy point defect structure analogous to well-known quantum defects in other materials that produce favorable optical and spin dynamics. First principles calculations confirm the thermodynamic stability and electronic structure of CuZn-VS. Temperature- and time-dependent optical properties of ZnS:Cu NCs show blueshifting luminescence and an anomalous plateau in the intensity dependence as temperature is increased from 19 K to 290 K, for which we propose an empirical dynamical model based on thermally-activated coupling between two manifolds of states inside the ZnS bandgap. Understanding of R-Cu emission dynamics, combined with a controlled synthesis method for obtaining R-Cu centers in colloidal NC hosts, will greatly facilitate the development of CuZn-VS and related complexes as quantum point defects in ZnS.},
keywords = {colloidal nanocrystals, color centers, First-principles calculations, impurity doping, Materials Physics, nanocrystals, photoluminescence, quantum dots, transition metals, ZnS},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2024

Shulevitz, Henry J.; Amirshaghaghi, Ahmad; Ouellet, Mathieu; Brustoloni, Caroline; Yang, Shengsong; Ng, Jonah J.; Huang, Tzu-Yung; Jishkariani, Davit; Murray, Christopher B.; Tsourkas, Andrew; Kagan, Cherie R.; Bassett, Lee C.
Nanodiamond emulsions for enhanced quantum sensing and click-chemistry conjugation Journal Article
In: ACS Applied Nano Materials, vol. 7, iss. 13, pp. 15334-15343, 2024.
@article{Shulevitz2024,
title = {Nanodiamond emulsions for enhanced quantum sensing and click-chemistry conjugation},
author = {Henry J. Shulevitz and Ahmad Amirshaghaghi and Mathieu Ouellet and Caroline Brustoloni and Shengsong Yang and Jonah J. Ng and Tzu-Yung Huang and Davit Jishkariani and Christopher B. Murray and Andrew Tsourkas and Cherie R. Kagan and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsanm.4c01699
https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.16530},
doi = {10.1021/acsanm.4c01699},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-06-29},
urldate = {2024-06-29},
journal = {ACS Applied Nano Materials},
volume = {7},
issue = {13},
pages = {15334-15343},
abstract = {Nanodiamonds containing nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers can serve as colloidal quantum sensors of local fields in biological and chemical environments. However, nanodiamond surfaces are challenging to modify without degrading their colloidal stability or the NV center’s optical and spin properties. We present a simple and general method to coat nanodiamonds with a thin emulsion layer that preserves their quantum features, maintains their colloidal stability, and provides functional groups for subsequent cross-linking and click-chemistry conjugation reactions. To demonstrate this technique, we decorated nanodiamonds with combinations of carboxyl- and azide-terminated amphiphiles that enable conjugation using two different strategies. A theoretical model is developed to understand the effect of the emulsion layer on the NV center’s spin lifetime, and T1 relaxometry is employed to quantify the nanodiamonds’ chemical sensitivity to paramagnetic ions. This general approach to nanodiamond surface functionalization will enable advances in quantum nanomedicine and biological sensing.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2023

Thompson, Sarah M.; Şahin, Cüneyt; Yang, Shengsong; Flatté, Michael E.; Murray, Christopher B.; Bassett, Lee C.; Kagan, Cherie R.
Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, 2023.
@article{Thompson2023,
title = {Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals},
author = {Sarah M. Thompson and Cüneyt Şahin and Shengsong Yang and Michael E. Flatté and Christopher B. Murray and Lee C. Bassett and Cherie R. Kagan},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.3c00191
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.04223},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.3c00191},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-03-09},
journal = {ACS Nano},
abstract = {Copper-doped zinc sulfide (ZnS:Cu) exhibits down-conversion luminescence in the UV, visible, and IR regions of the electromagnetic spectrum; the visible red, green, and blue emission is referred to as R-Cu, G-Cu, and B-Cu, respectively. The sub-bandgap emission arises from optical transitions between localized electronic states created by point defects, making ZnS:Cu a prolific phosphor material and an intriguing candidate material for quantum information science, where point defects excel as single-photon sources and spin qubits. Colloidal nanocrystals (NCs) of ZnS:Cu are particularly interesting as hosts for the creation, isolation, and measurement of quantum defects, since their size, composition, and surface chemistry can be precisely tailored for bio-sensing and opto-electronic applications. Here, we present a method for synthesizing colloidal ZnS:Cu NCs that emit primarily R-Cu, which has been proposed to arise from the CuZn-VS complex, an impurity-vacancy point defect structure analogous to well-known quantum defects in other materials that produce favorable optical and spin dynamics. First principles calculations confirm the thermodynamic stability and electronic structure of CuZn-VS. Temperature- and time-dependent optical properties of ZnS:Cu NCs show blueshifting luminescence and an anomalous plateau in the intensity dependence as temperature is increased from 19 K to 290 K, for which we propose an empirical dynamical model based on thermally-activated coupling between two manifolds of states inside the ZnS bandgap. Understanding of R-Cu emission dynamics, combined with a controlled synthesis method for obtaining R-Cu centers in colloidal NC hosts, will greatly facilitate the development of CuZn-VS and related complexes as quantum point defects in ZnS.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Select publications before 2014
- “All-optical control of a solid-state spin using coherent dark states”, C. G. Yale, B. B. Buckley, D. J. Christle, G. Burkard, F. J. Heremans, L. C. Bassett, and D. D. Awschalom, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 7595 (2013).
- “Quantum spintronics: Engineering and manipulating atom-like spins in semiconductors”, D.D. Awschalom, L.C. Bassett, A.S. Dzurak, E.L. Hu and J.R. Petta, Science 339, 1174 (2013).
Related article: “The Future of Quantum Information Processing”, J. Stajic, Science 339, 1163 (2013).
- “Engineering and quantum control of single spins in semiconductors”, D.M. Toyli, L.C. Bassett, B.B. Buckley, G. Calusine and D.D. Awschalom, MRS Bulletin 38, 139 (2013).
- “Engineering shallow spins in diamond with nitrogen delta-doping”, K. Ohno, F. J. Heremans, L. C. Bassett, B. A. Myers, D. M. Toyli, A. C. Bleszynski-Jayich, C. J. Palmstrøm, and D. D. Awschalom, Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 082413 (2012).
- “Electrical tuning of single nitrogen-vacancy center optical transitions enhanced by photoinduced fields”, L. C. Bassett, F. J. Heremans, C. G. Yale, B. B. Buckley, and D. D. Awschalom, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 266403 (2011).
- “Spin-light coherence for single-spin measurement and control in diamond”, B. B. Buckley, G. D. Fuchs, L. C. Bassett, and D. D. Awschalom, Science 330, 1212 (2010).
Related article: “Quantum measurement and control of single spins in diamond”, Science 330, 1188 (2010).