Patel, Raj N.; Fishman, Rebecca E. K.; Huang, Tzu-Yung; Gusdorff, Jordan A.; Fehr, David A.; Hopper, David A.; Breitweiser, S. Alex; Porat, Benjamin; Flatté, Michael E.; Bassett, Lee C.
Room Temperature Dynamics of an Optically Addressable Single Spin in Hexagonal Boron Nitride Journal Article
In: Nano Letters, vol. 24, iss. 25, pp. 7623-7628, 2024.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 2-dimensional systems, First-principles calculations, photon emission correlation spectroscopy, photon statistics, point defects
@article{Patel2024,
title = {Room Temperature Dynamics of an Optically Addressable Single Spin in Hexagonal Boron Nitride},
author = {Raj N. Patel and Rebecca E. K. Fishman and Tzu-Yung Huang and Jordan A. Gusdorff and David A. Fehr and David A. Hopper and S. Alex Breitweiser and Benjamin Porat and Michael E. Flatté and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01333
https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.05604},
doi = {10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01333},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-06-11},
urldate = {2024-06-11},
journal = {Nano Letters},
volume = {24},
issue = {25},
pages = {7623-7628},
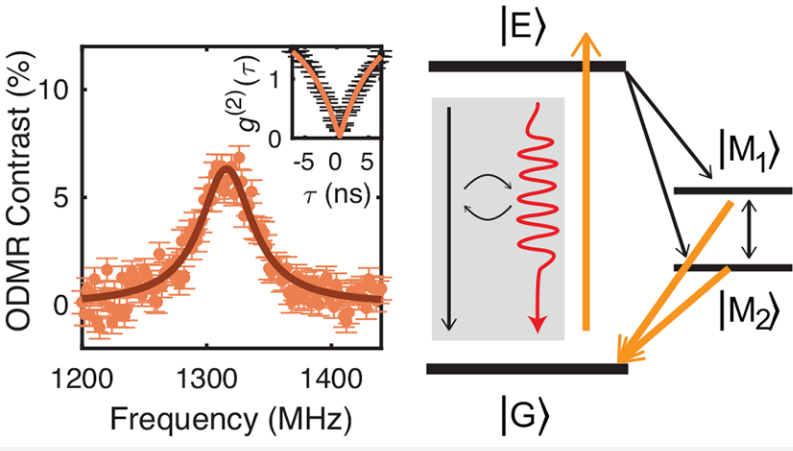
abstract = {Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) hosts pure single-photon emitters that have shown evidence of optically detected electronic spin dynamics. However, the electrical and chemical structures of these optically addressable spins are unknown, and the nature of their spin-optical interactions remains mysterious. Here, we use time-domain optical and microwave experiments to characterize a single emitter in h-BN exhibiting room temperature optically detected magnetic resonance. Using dynamical simulations, we constrain and quantify transition rates in the model, and we design optical control protocols that optimize the signal-to-noise ratio for spin readout. This constitutes a necessary step toward quantum control of spin states in h-BN.},
keywords = {2-dimensional systems, First-principles calculations, photon emission correlation spectroscopy, photon statistics, point defects},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Thompson, Sarah M.; Şahin, Cüneyt; Yang, Shengsong; Flatté, Michael E.; Murray, Christopher B.; Bassett, Lee C.; Kagan, Cherie R.
Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, 2023.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: colloidal nanocrystals, color centers, First-principles calculations, impurity doping, Materials Physics, nanocrystals, photoluminescence, quantum dots, transition metals, ZnS
@article{Thompson2023,
title = {Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals},
author = {Sarah M. Thompson and Cüneyt Şahin and Shengsong Yang and Michael E. Flatté and Christopher B. Murray and Lee C. Bassett and Cherie R. Kagan},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.3c00191
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.04223},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.3c00191},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-03-09},
journal = {ACS Nano},
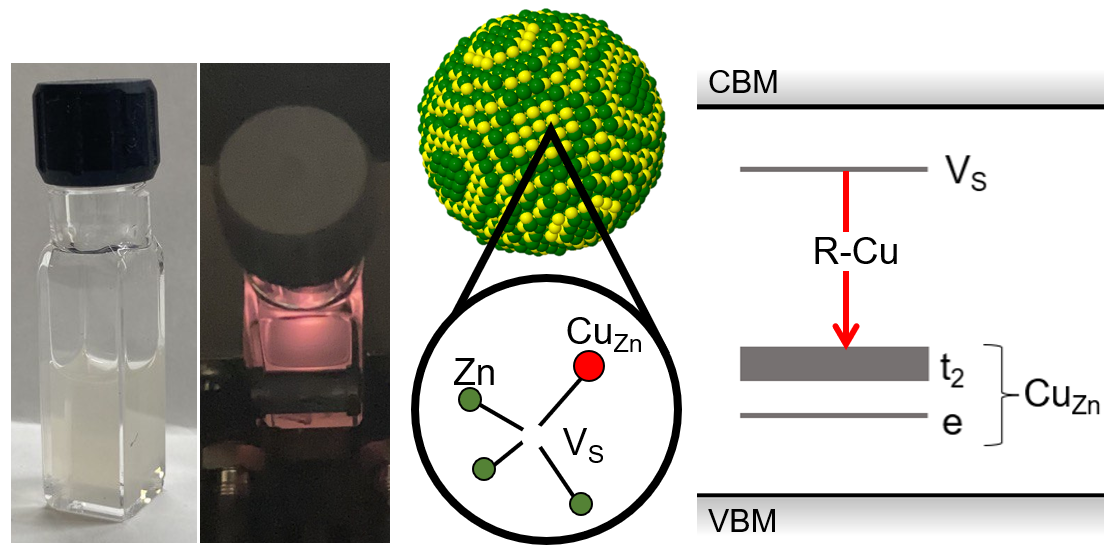
abstract = {Copper-doped zinc sulfide (ZnS:Cu) exhibits down-conversion luminescence in the UV, visible, and IR regions of the electromagnetic spectrum; the visible red, green, and blue emission is referred to as R-Cu, G-Cu, and B-Cu, respectively. The sub-bandgap emission arises from optical transitions between localized electronic states created by point defects, making ZnS:Cu a prolific phosphor material and an intriguing candidate material for quantum information science, where point defects excel as single-photon sources and spin qubits. Colloidal nanocrystals (NCs) of ZnS:Cu are particularly interesting as hosts for the creation, isolation, and measurement of quantum defects, since their size, composition, and surface chemistry can be precisely tailored for bio-sensing and opto-electronic applications. Here, we present a method for synthesizing colloidal ZnS:Cu NCs that emit primarily R-Cu, which has been proposed to arise from the CuZn-VS complex, an impurity-vacancy point defect structure analogous to well-known quantum defects in other materials that produce favorable optical and spin dynamics. First principles calculations confirm the thermodynamic stability and electronic structure of CuZn-VS. Temperature- and time-dependent optical properties of ZnS:Cu NCs show blueshifting luminescence and an anomalous plateau in the intensity dependence as temperature is increased from 19 K to 290 K, for which we propose an empirical dynamical model based on thermally-activated coupling between two manifolds of states inside the ZnS bandgap. Understanding of R-Cu emission dynamics, combined with a controlled synthesis method for obtaining R-Cu centers in colloidal NC hosts, will greatly facilitate the development of CuZn-VS and related complexes as quantum point defects in ZnS.},
keywords = {colloidal nanocrystals, color centers, First-principles calculations, impurity doping, Materials Physics, nanocrystals, photoluminescence, quantum dots, transition metals, ZnS},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Fishman, Rebecca E. K.; Patel, Raj N.; Hopper, David A.; Huang, Tzu-Yung; Bassett, Lee C.
Photon emission correlation spectroscopy as an analytical tool for quantum defects Journal Article
In: PRX Quantum, vol. 4, pp. 010202, 2023.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: First-principles calculations, Materials Physics, Optics, photon emission correlation spectroscopy, photon statistics, point defects, quantum defects
@article{Fishman2021,
title = {Photon emission correlation spectroscopy as an analytical tool for quantum defects},
author = {Rebecca E. K. Fishman and Raj N. Patel and David A. Hopper and Tzu-Yung Huang and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prxquantum/abstract/10.1103/PRXQuantum.4.010202
https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.01252},
doi = {10.1103/PRXQuantum.4.010202},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-03-06},
journal = {PRX Quantum},
volume = {4},
pages = {010202},
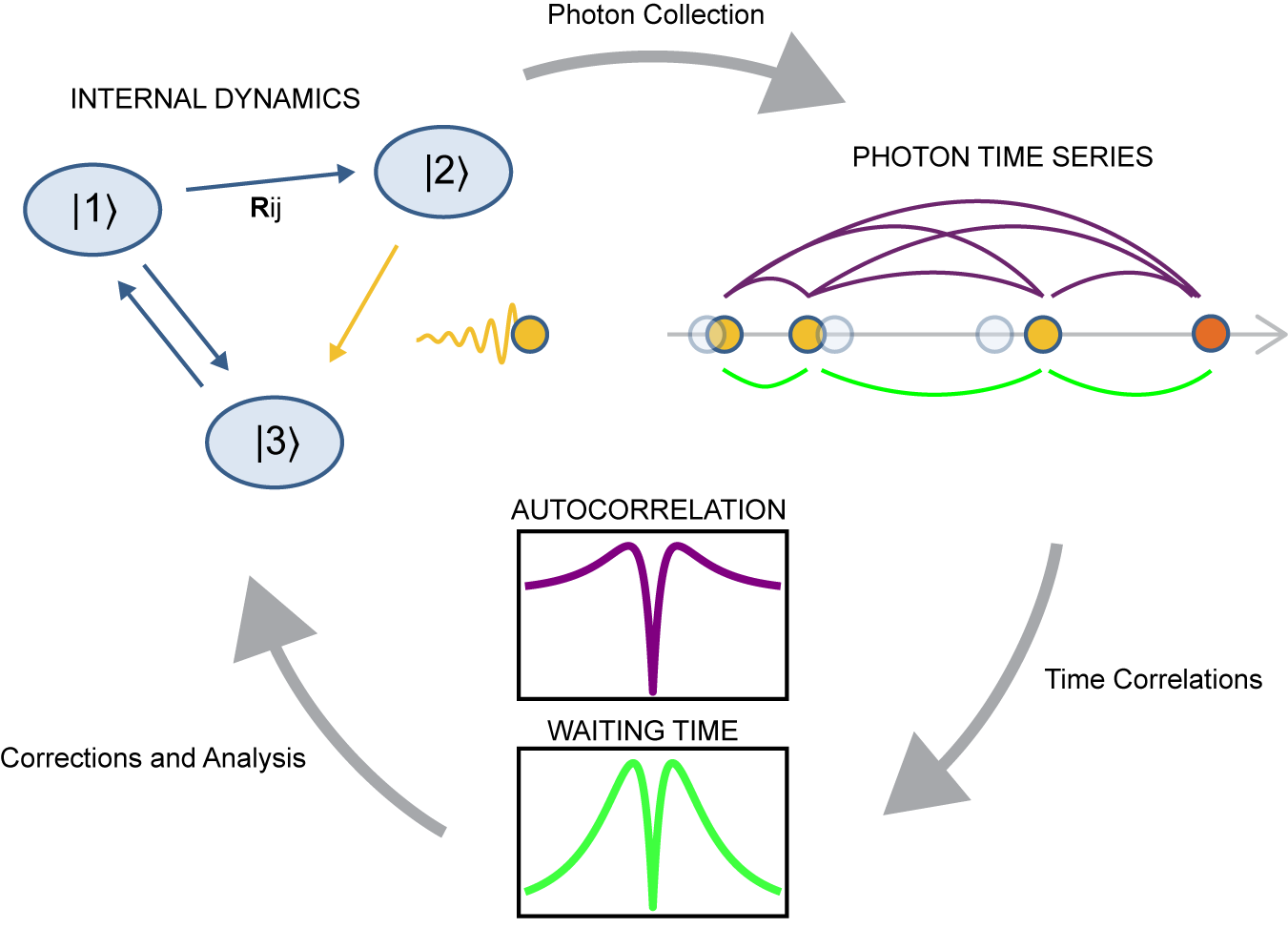
abstract = {Photon emission correlation spectroscopy has a long history in the study of atoms, molecules, and, more recently, solid-state quantum defects. In solid-state systems, its most common use is as an indicator of single-photon emission, a key property for quantum technology. However, photon correlation data can provide a wealth of information about quantum emitters beyond their single-photon purity−information that can reveal details about an emitter's electronic structure and optical dynamics that are hidden by other spectroscopy techniques. We present a standardized framework for using photon emission correlation spectroscopy to study quantum emitters, including discussion of theory, data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation. We highlight nuances and best practices regarding the commonly used g(2)(τ=0)<0.5 test for single-photon emission. Finally, we illustrate how this experimental technique can be paired with optical dynamics simulations to formulate an electronic model for unknown quantum emitters, enabling the design of quantum control protocols and assessment of their suitability for quantum information science applications.},
keywords = {First-principles calculations, Materials Physics, Optics, photon emission correlation spectroscopy, photon statistics, point defects, quantum defects},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
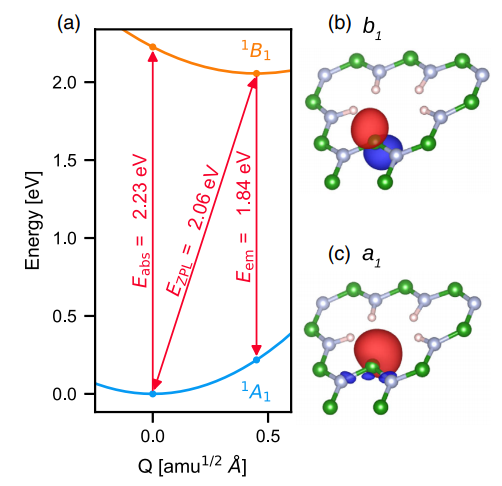
Turiansky, M E; Alkauskas, A; Bassett, L C; de Walle, Van C G
Dangling bonds in hexagonal boron nitride as single-photon emitters Journal Article
In: Physical Review Letters, vol. 123, no. 12, pp. 127401, 2019, ISSN: 1079-7114.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: 2-dimensional systems, Condensed Matter, First-principles calculations, Optical absorption spectroscopy, Optical microcavities, optical sources, point defects, Quantum wells, Semiconductor compounds
@article{Turiansky2019,
title = {Dangling bonds in hexagonal boron nitride as single-photon emitters},
author = {M E Turiansky and A Alkauskas and L C Bassett and Van C G de Walle},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.127401},
doi = {10.1103},
issn = {1079-7114},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-09-16},
journal = {Physical Review Letters},
volume = {123},
number = {12},
pages = {127401},
abstract = {Hexagonal boron nitride has been found to host color centers that exhibit single-photon emission, but the microscopic origin of these emitters is unknown. We propose boron dangling bonds as the likely source of the observed single-photon emission around 2 eV. An optical transition where an electron is excited from a doubly occupied boron dangling bond to a localized B pz state gives rise to a zero-phonon line of 2.06 eV and emission with a Huang-Rhys factor of 2.3. This transition is linearly polarized with the absorptive and emissive dipole aligned. Because of the energetic position of the states within the band gap, indirect excitation through the conduction band will occur for sufficiently large excitation energies, leading to the misalignment of the absorptive and emissive dipoles seen in experiment. Our calculations predict a singlet ground state and the existence of a metastable triplet state, in agreement with experiment.},
keywords = {2-dimensional systems, Condensed Matter, First-principles calculations, Optical absorption spectroscopy, Optical microcavities, optical sources, point defects, Quantum wells, Semiconductor compounds},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2024

Patel, Raj N.; Fishman, Rebecca E. K.; Huang, Tzu-Yung; Gusdorff, Jordan A.; Fehr, David A.; Hopper, David A.; Breitweiser, S. Alex; Porat, Benjamin; Flatté, Michael E.; Bassett, Lee C.
Room Temperature Dynamics of an Optically Addressable Single Spin in Hexagonal Boron Nitride Journal Article
In: Nano Letters, vol. 24, iss. 25, pp. 7623-7628, 2024.
@article{Patel2024,
title = {Room Temperature Dynamics of an Optically Addressable Single Spin in Hexagonal Boron Nitride},
author = {Raj N. Patel and Rebecca E. K. Fishman and Tzu-Yung Huang and Jordan A. Gusdorff and David A. Fehr and David A. Hopper and S. Alex Breitweiser and Benjamin Porat and Michael E. Flatté and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01333
https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.05604},
doi = {10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01333},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-06-11},
urldate = {2024-06-11},
journal = {Nano Letters},
volume = {24},
issue = {25},
pages = {7623-7628},
abstract = {Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) hosts pure single-photon emitters that have shown evidence of optically detected electronic spin dynamics. However, the electrical and chemical structures of these optically addressable spins are unknown, and the nature of their spin-optical interactions remains mysterious. Here, we use time-domain optical and microwave experiments to characterize a single emitter in h-BN exhibiting room temperature optically detected magnetic resonance. Using dynamical simulations, we constrain and quantify transition rates in the model, and we design optical control protocols that optimize the signal-to-noise ratio for spin readout. This constitutes a necessary step toward quantum control of spin states in h-BN.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2023

Thompson, Sarah M.; Şahin, Cüneyt; Yang, Shengsong; Flatté, Michael E.; Murray, Christopher B.; Bassett, Lee C.; Kagan, Cherie R.
Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, 2023.
@article{Thompson2023,
title = {Red Emission from Copper-Vacancy Color Centers in Zinc Sulfide Colloidal Nanocrystals},
author = {Sarah M. Thompson and Cüneyt Şahin and Shengsong Yang and Michael E. Flatté and Christopher B. Murray and Lee C. Bassett and Cherie R. Kagan},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsnano.3c00191
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.04223},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.3c00191},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-03-09},
journal = {ACS Nano},
abstract = {Copper-doped zinc sulfide (ZnS:Cu) exhibits down-conversion luminescence in the UV, visible, and IR regions of the electromagnetic spectrum; the visible red, green, and blue emission is referred to as R-Cu, G-Cu, and B-Cu, respectively. The sub-bandgap emission arises from optical transitions between localized electronic states created by point defects, making ZnS:Cu a prolific phosphor material and an intriguing candidate material for quantum information science, where point defects excel as single-photon sources and spin qubits. Colloidal nanocrystals (NCs) of ZnS:Cu are particularly interesting as hosts for the creation, isolation, and measurement of quantum defects, since their size, composition, and surface chemistry can be precisely tailored for bio-sensing and opto-electronic applications. Here, we present a method for synthesizing colloidal ZnS:Cu NCs that emit primarily R-Cu, which has been proposed to arise from the CuZn-VS complex, an impurity-vacancy point defect structure analogous to well-known quantum defects in other materials that produce favorable optical and spin dynamics. First principles calculations confirm the thermodynamic stability and electronic structure of CuZn-VS. Temperature- and time-dependent optical properties of ZnS:Cu NCs show blueshifting luminescence and an anomalous plateau in the intensity dependence as temperature is increased from 19 K to 290 K, for which we propose an empirical dynamical model based on thermally-activated coupling between two manifolds of states inside the ZnS bandgap. Understanding of R-Cu emission dynamics, combined with a controlled synthesis method for obtaining R-Cu centers in colloidal NC hosts, will greatly facilitate the development of CuZn-VS and related complexes as quantum point defects in ZnS.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Fishman, Rebecca E. K.; Patel, Raj N.; Hopper, David A.; Huang, Tzu-Yung; Bassett, Lee C.
Photon emission correlation spectroscopy as an analytical tool for quantum defects Journal Article
In: PRX Quantum, vol. 4, pp. 010202, 2023.
@article{Fishman2021,
title = {Photon emission correlation spectroscopy as an analytical tool for quantum defects},
author = {Rebecca E. K. Fishman and Raj N. Patel and David A. Hopper and Tzu-Yung Huang and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prxquantum/abstract/10.1103/PRXQuantum.4.010202
https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.01252},
doi = {10.1103/PRXQuantum.4.010202},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-03-06},
journal = {PRX Quantum},
volume = {4},
pages = {010202},
abstract = {Photon emission correlation spectroscopy has a long history in the study of atoms, molecules, and, more recently, solid-state quantum defects. In solid-state systems, its most common use is as an indicator of single-photon emission, a key property for quantum technology. However, photon correlation data can provide a wealth of information about quantum emitters beyond their single-photon purity−information that can reveal details about an emitter's electronic structure and optical dynamics that are hidden by other spectroscopy techniques. We present a standardized framework for using photon emission correlation spectroscopy to study quantum emitters, including discussion of theory, data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation. We highlight nuances and best practices regarding the commonly used g(2)(τ=0)<0.5 test for single-photon emission. Finally, we illustrate how this experimental technique can be paired with optical dynamics simulations to formulate an electronic model for unknown quantum emitters, enabling the design of quantum control protocols and assessment of their suitability for quantum information science applications.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2019

Turiansky, M E; Alkauskas, A; Bassett, L C; de Walle, Van C G
Dangling bonds in hexagonal boron nitride as single-photon emitters Journal Article
In: Physical Review Letters, vol. 123, no. 12, pp. 127401, 2019, ISSN: 1079-7114.
@article{Turiansky2019,
title = {Dangling bonds in hexagonal boron nitride as single-photon emitters},
author = {M E Turiansky and A Alkauskas and L C Bassett and Van C G de Walle},
url = {https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.127401},
doi = {10.1103},
issn = {1079-7114},
year = {2019},
date = {2019-09-16},
journal = {Physical Review Letters},
volume = {123},
number = {12},
pages = {127401},
abstract = {Hexagonal boron nitride has been found to host color centers that exhibit single-photon emission, but the microscopic origin of these emitters is unknown. We propose boron dangling bonds as the likely source of the observed single-photon emission around 2 eV. An optical transition where an electron is excited from a doubly occupied boron dangling bond to a localized B pz state gives rise to a zero-phonon line of 2.06 eV and emission with a Huang-Rhys factor of 2.3. This transition is linearly polarized with the absorptive and emissive dipole aligned. Because of the energetic position of the states within the band gap, indirect excitation through the conduction band will occur for sufficiently large excitation energies, leading to the misalignment of the absorptive and emissive dipoles seen in experiment. Our calculations predict a singlet ground state and the existence of a metastable triplet state, in agreement with experiment.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Select publications before 2014
- “All-optical control of a solid-state spin using coherent dark states”, C. G. Yale, B. B. Buckley, D. J. Christle, G. Burkard, F. J. Heremans, L. C. Bassett, and D. D. Awschalom, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 7595 (2013).
- “Quantum spintronics: Engineering and manipulating atom-like spins in semiconductors”, D.D. Awschalom, L.C. Bassett, A.S. Dzurak, E.L. Hu and J.R. Petta, Science 339, 1174 (2013).
Related article: “The Future of Quantum Information Processing”, J. Stajic, Science 339, 1163 (2013).
- “Engineering and quantum control of single spins in semiconductors”, D.M. Toyli, L.C. Bassett, B.B. Buckley, G. Calusine and D.D. Awschalom, MRS Bulletin 38, 139 (2013).
- “Engineering shallow spins in diamond with nitrogen delta-doping”, K. Ohno, F. J. Heremans, L. C. Bassett, B. A. Myers, D. M. Toyli, A. C. Bleszynski-Jayich, C. J. Palmstrøm, and D. D. Awschalom, Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 082413 (2012).
- “Electrical tuning of single nitrogen-vacancy center optical transitions enhanced by photoinduced fields”, L. C. Bassett, F. J. Heremans, C. G. Yale, B. B. Buckley, and D. D. Awschalom, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 266403 (2011).
- “Spin-light coherence for single-spin measurement and control in diamond”, B. B. Buckley, G. D. Fuchs, L. C. Bassett, and D. D. Awschalom, Science 330, 1212 (2010).
Related article: “Quantum measurement and control of single spins in diamond”, Science 330, 1188 (2010).