Narun, Leah R.; Fishman, Rebecca E. K.; Shulevitz, Henry J.; Patel, Raj N.; Bassett, Lee C.
Efficient Analysis of Photoluminescence Images for the Classification of Single-Photon Emitters Journal Article
In: ACS Photonics, vol. 9, no. 11, pp. 3540–3549, 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: nanodiamond assembly, neurophysiology, nitrides, photon emission correlation spectroscopy, photon statistics
@article{Narun2021,
title = {Efficient Analysis of Photoluminescence Images for the Classification of Single-Photon Emitters},
author = {Leah R. Narun and Rebecca E. K. Fishman and Henry J. Shulevitz and Raj N. Patel and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsphotonics.2c00795
https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.05654},
doi = {10.1021/acsphotonics.2c00795},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-10-31},
journal = {ACS Photonics},
volume = {9},
number = {11},
pages = {3540–3549},
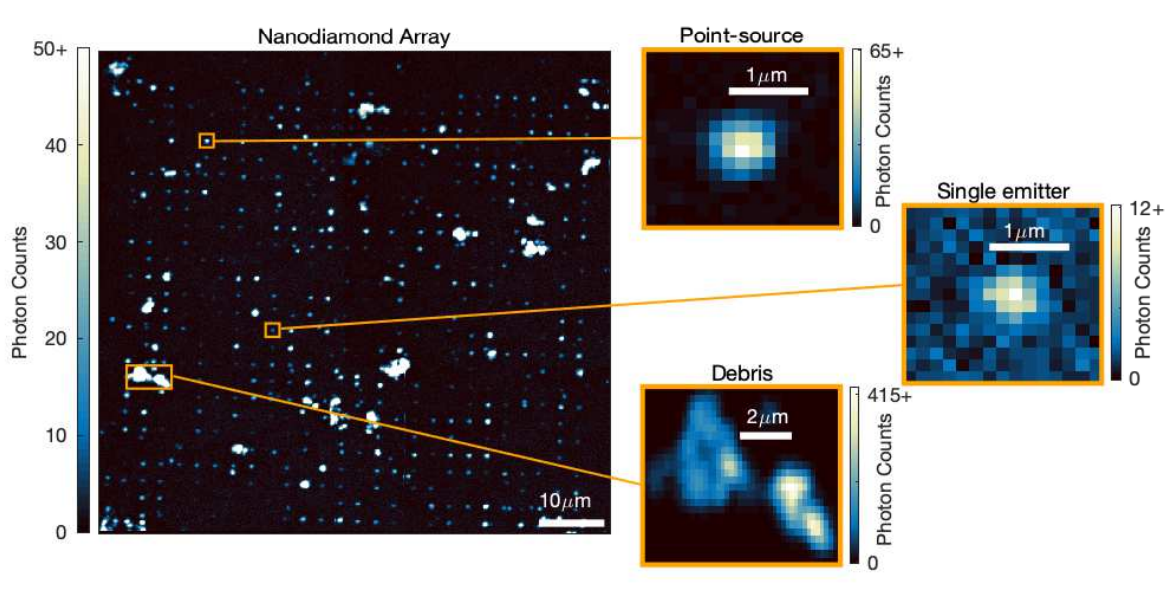
abstract = {Solid-state single-photon emitters (SPE) are a basis for emerging technologies such as quantum communication and quantum sensing. SPE based on fluorescent point defects are ubiquitous in semiconductors and insulators, and new systems with desirable properties for quantum information science may exist amongst the vast number of unexplored defects. However, the characterization of new SPE typically relies on time-consuming techniques for identifying point source emitters by eye in photoluminescence (PL) images. This manual strategy is a bottleneck for discovering new SPE, motivating a more efficient method for characterizing emitters in PL images. Here we present a quantitative method using image analysis and regression fitting to automatically identify Gaussian emitters in PL images and classify them according to their stability, shape, and intensity relative to the background. We demonstrate efficient emitter classification for SPEs in nanodiamond arrays and hexagonal boron nitride flakes. Adaptive criteria detect SPE in both samples despite variation in emitter intensity, stability, and background features. The detection criteria can be tuned for specific material systems and experimental setups to accommodate the diverse properties of SPE.},
keywords = {nanodiamond assembly, neurophysiology, nitrides, photon emission correlation spectroscopy, photon statistics},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
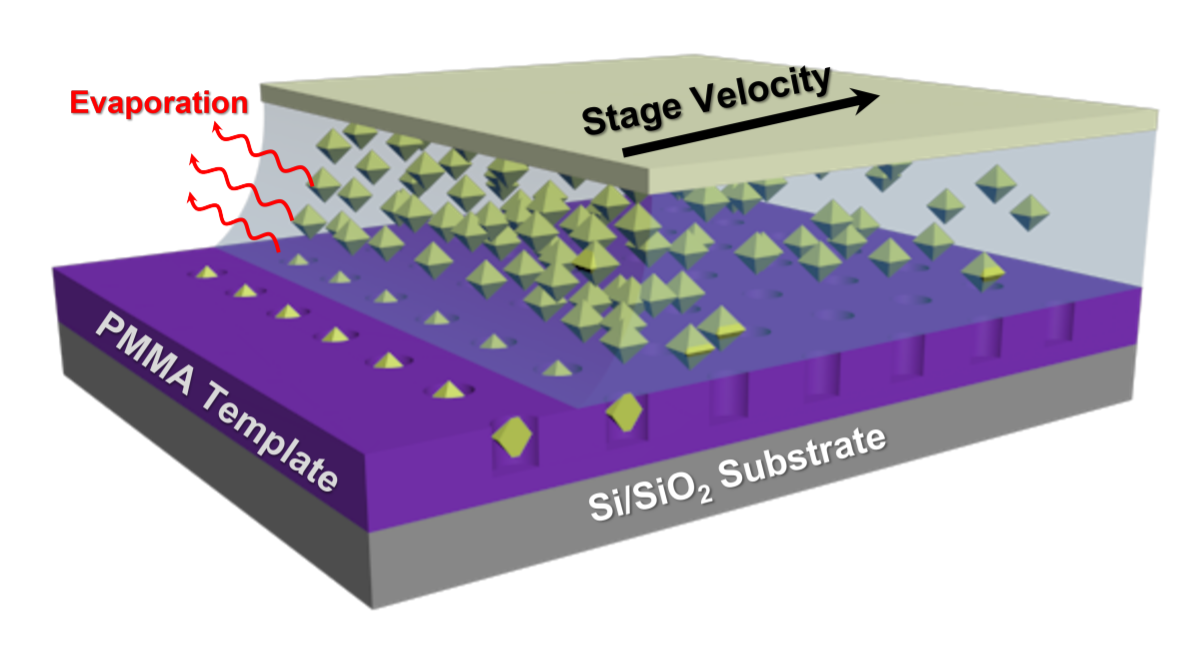
Shulevitz, Henry J.; Huang, Tzu-Yung; Xu, Jun; Neuhaus, Steven; Patel, Raj N.; Lee C. Bassett, Cherie R. Kagan
Template-Assisted Self Assembly of Fluorescent Nanodiamonds for Scalable Quantum Technologies Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 1847–1856, 2022.
Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Condensed Matter, diamond NV center, nanodiamond assembly, Nanophotonics
@article{Shulevitz2021,
title = {Template-Assisted Self Assembly of Fluorescent Nanodiamonds for Scalable Quantum Technologies},
author = {Henry J. Shulevitz and Tzu-Yung Huang and Jun Xu and Steven Neuhaus and Raj N. Patel and Lee C. Bassett, Cherie R. Kagan},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14921},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.1c09839},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-13},
journal = {ACS Nano},
volume = {16},
number = {2},
pages = {1847–1856},
abstract = {Milled nanodiamonds containing nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers provide an excellent platform for sensing applications as they are optically robust, have nanoscale quantum sensitivity, and form colloidal dispersions which enable bottom-up assembly techniques for device integration. However, variations in their size, shape, and surface chemistry limit the ability to position individual nanodiamonds and statistically study properties that affect their optical and quantum characteristics. Here, we present a scalable strategy to form ordered arrays of nanodiamonds using capillary-driven, template-assisted self assembly. This method enables the precise spatial arrangement of isolated nanodiamonds with diameters below 50 nm across millimeter-scale areas. Measurements of over 200 assembled nanodiamonds yield a statistical understanding of their structural, optical, and quantum properties. The NV centers' spin and charge properties are uncorrelated with nanodiamond size, but rather are consistent with heterogeneity in their nanoscale environment. This flexible assembly method, together with improved understanding of the material, will enable the integration of nanodiamonds into future quantum photonic and electronic devices.},
keywords = {Condensed Matter, diamond NV center, nanodiamond assembly, Nanophotonics},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2022

Narun, Leah R.; Fishman, Rebecca E. K.; Shulevitz, Henry J.; Patel, Raj N.; Bassett, Lee C.
Efficient Analysis of Photoluminescence Images for the Classification of Single-Photon Emitters Journal Article
In: ACS Photonics, vol. 9, no. 11, pp. 3540–3549, 2022.
@article{Narun2021,
title = {Efficient Analysis of Photoluminescence Images for the Classification of Single-Photon Emitters},
author = {Leah R. Narun and Rebecca E. K. Fishman and Henry J. Shulevitz and Raj N. Patel and Lee C. Bassett},
url = {https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsphotonics.2c00795
https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.05654},
doi = {10.1021/acsphotonics.2c00795},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-10-31},
journal = {ACS Photonics},
volume = {9},
number = {11},
pages = {3540–3549},
abstract = {Solid-state single-photon emitters (SPE) are a basis for emerging technologies such as quantum communication and quantum sensing. SPE based on fluorescent point defects are ubiquitous in semiconductors and insulators, and new systems with desirable properties for quantum information science may exist amongst the vast number of unexplored defects. However, the characterization of new SPE typically relies on time-consuming techniques for identifying point source emitters by eye in photoluminescence (PL) images. This manual strategy is a bottleneck for discovering new SPE, motivating a more efficient method for characterizing emitters in PL images. Here we present a quantitative method using image analysis and regression fitting to automatically identify Gaussian emitters in PL images and classify them according to their stability, shape, and intensity relative to the background. We demonstrate efficient emitter classification for SPEs in nanodiamond arrays and hexagonal boron nitride flakes. Adaptive criteria detect SPE in both samples despite variation in emitter intensity, stability, and background features. The detection criteria can be tuned for specific material systems and experimental setups to accommodate the diverse properties of SPE.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

Shulevitz, Henry J.; Huang, Tzu-Yung; Xu, Jun; Neuhaus, Steven; Patel, Raj N.; Lee C. Bassett, Cherie R. Kagan
Template-Assisted Self Assembly of Fluorescent Nanodiamonds for Scalable Quantum Technologies Journal Article
In: ACS Nano, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 1847–1856, 2022.
@article{Shulevitz2021,
title = {Template-Assisted Self Assembly of Fluorescent Nanodiamonds for Scalable Quantum Technologies},
author = {Henry J. Shulevitz and Tzu-Yung Huang and Jun Xu and Steven Neuhaus and Raj N. Patel and Lee C. Bassett, Cherie R. Kagan},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.14921},
doi = {10.1021/acsnano.1c09839},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-13},
journal = {ACS Nano},
volume = {16},
number = {2},
pages = {1847–1856},
abstract = {Milled nanodiamonds containing nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers provide an excellent platform for sensing applications as they are optically robust, have nanoscale quantum sensitivity, and form colloidal dispersions which enable bottom-up assembly techniques for device integration. However, variations in their size, shape, and surface chemistry limit the ability to position individual nanodiamonds and statistically study properties that affect their optical and quantum characteristics. Here, we present a scalable strategy to form ordered arrays of nanodiamonds using capillary-driven, template-assisted self assembly. This method enables the precise spatial arrangement of isolated nanodiamonds with diameters below 50 nm across millimeter-scale areas. Measurements of over 200 assembled nanodiamonds yield a statistical understanding of their structural, optical, and quantum properties. The NV centers' spin and charge properties are uncorrelated with nanodiamond size, but rather are consistent with heterogeneity in their nanoscale environment. This flexible assembly method, together with improved understanding of the material, will enable the integration of nanodiamonds into future quantum photonic and electronic devices.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Select publications before 2014
- “All-optical control of a solid-state spin using coherent dark states”, C. G. Yale, B. B. Buckley, D. J. Christle, G. Burkard, F. J. Heremans, L. C. Bassett, and D. D. Awschalom, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 7595 (2013).
- “Quantum spintronics: Engineering and manipulating atom-like spins in semiconductors”, D.D. Awschalom, L.C. Bassett, A.S. Dzurak, E.L. Hu and J.R. Petta, Science 339, 1174 (2013).
Related article: “The Future of Quantum Information Processing”, J. Stajic, Science 339, 1163 (2013).
- “Engineering and quantum control of single spins in semiconductors”, D.M. Toyli, L.C. Bassett, B.B. Buckley, G. Calusine and D.D. Awschalom, MRS Bulletin 38, 139 (2013).
- “Engineering shallow spins in diamond with nitrogen delta-doping”, K. Ohno, F. J. Heremans, L. C. Bassett, B. A. Myers, D. M. Toyli, A. C. Bleszynski-Jayich, C. J. Palmstrøm, and D. D. Awschalom, Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 082413 (2012).
- “Electrical tuning of single nitrogen-vacancy center optical transitions enhanced by photoinduced fields”, L. C. Bassett, F. J. Heremans, C. G. Yale, B. B. Buckley, and D. D. Awschalom, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 266403 (2011).
- “Spin-light coherence for single-spin measurement and control in diamond”, B. B. Buckley, G. D. Fuchs, L. C. Bassett, and D. D. Awschalom, Science 330, 1212 (2010).
Related article: “Quantum measurement and control of single spins in diamond”, Science 330, 1188 (2010).